System Calls
System calls are programming interfaces provided by the OS Kernel for users to access kernel services
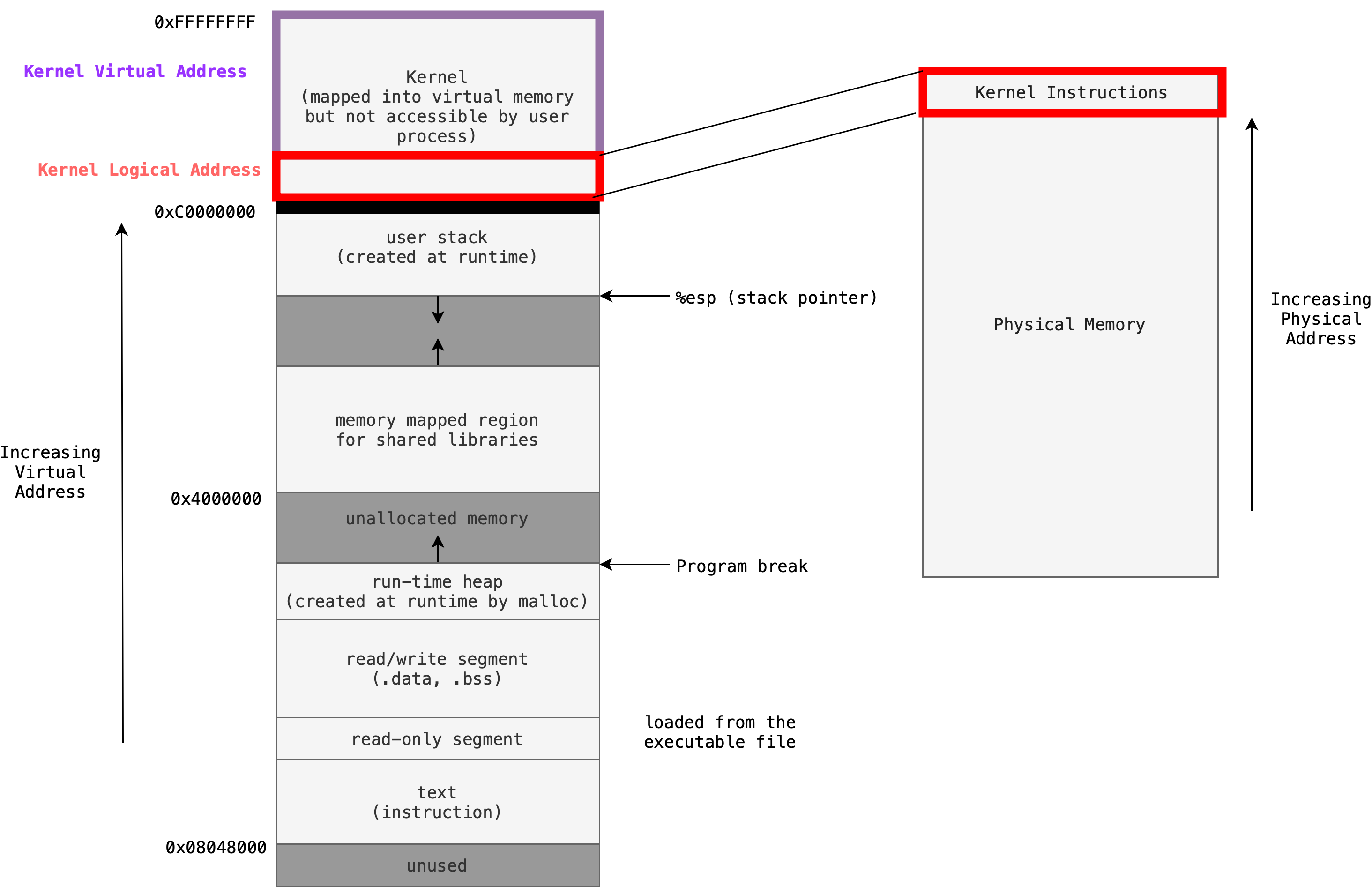
Kernel is divided into two spaces, logical and virtual (aka lowmem and vmalloc). In lowmem, the VA are mapped to PA with just an offset (X+C). This mapping is determined during a boot, and never changes. The kernel virtual address area (vmalloc) is used for non contiguous PA so that it is easier to allocate them
- dynamic, on demand
- On each allocation, a series of locations of PP are found for the corresponding kernel VP, and the pagetable is modified to create the mapping
- This makes it unsuitable for DMA
API is an interface that provides a way to interact with the underlying library2 that makes the system calls, often named the same as the system calls they invoke.
Parameters to syscalls can be passed through:
- Registers, (fast, limited by # of regs).
- Stack (slower, not limited by # of regs)
- Block: pointer to physical contiguous block of memory with all the args (same as stack)
Types of System Calls¶
- Process Control: load, create, start, pause, terminate processes, get and set process attributes, wait for time, wait for event, signal event, aloocate and free memory
- File Manipulation: create, delete, rename, open, close, read, write, copy, move
- Device Manipulation: request and release device, read, write, move device, get and set device attributes, logically attach or detach attributes
- Information Maintenance: get or set time and date, system data, process, file, device attributes
- Communication: create/delete pipes, send/receive packets through network, transfer status information, attach/detach remote devices
- Protection: set network enc protocs
Blocking vs Non Blocking Calls¶
A system call is blocking if the callee process must wait for the system call to return before it can continue its execution
input() is a blocking system call. If no input is ready when the call is made, then the process yields and other processes are scheduled.
A non blocking system call is one which can return immediately without completing I/O (async_load)
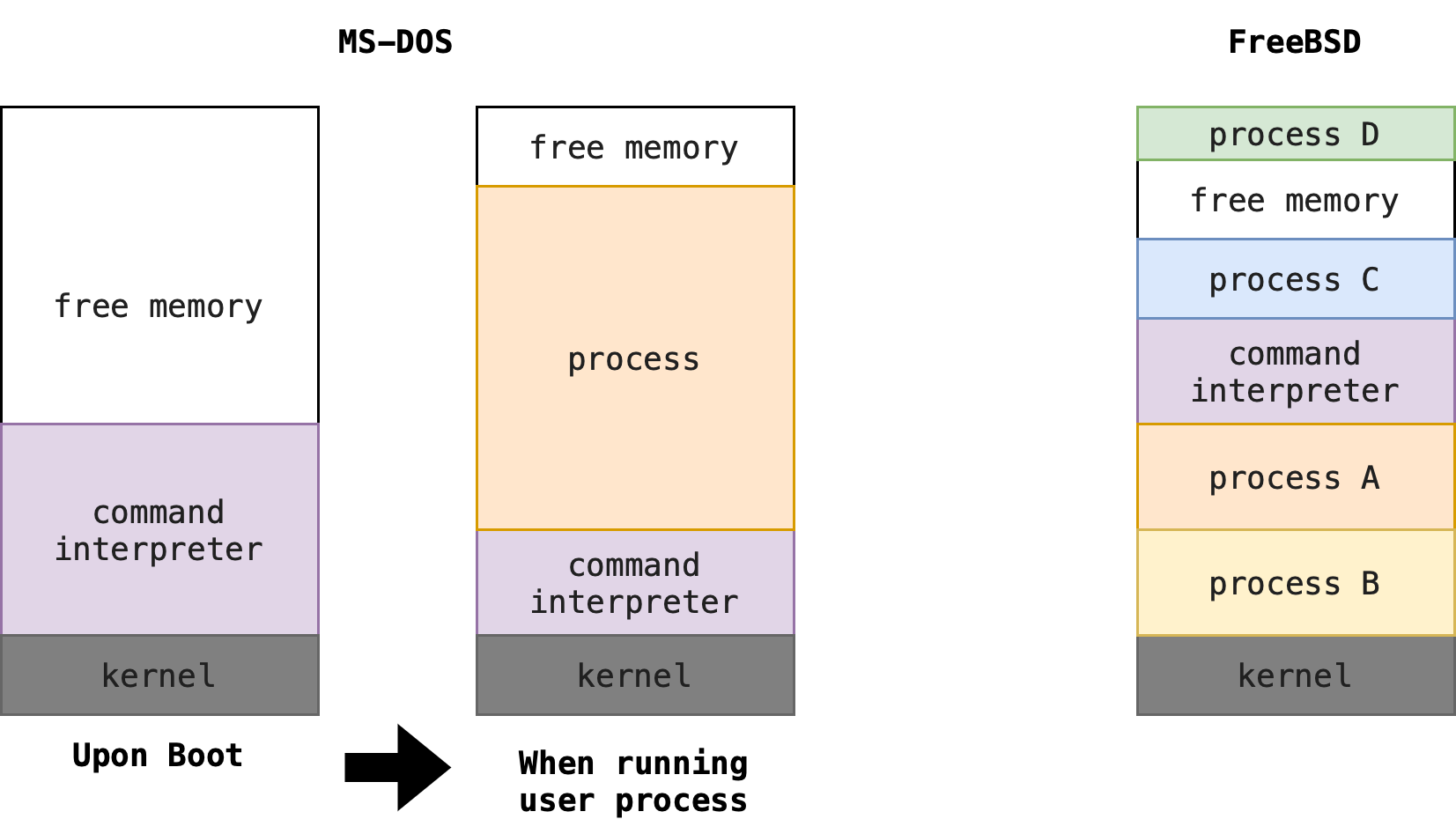
Single Tasking System¶
MS-DOS
- Overwrites itself
- Runs program
- Rewrites itself from disk
Multi Tasking System¶
FreeBSD
- Uses
fork()andexec()syscalls - Kernel resp for context switching and timesharing